What is Artificial Intelligence? Understanding the Basics of AI

When I started my career, I was just curious about how technology works, but with time, tech trends ignited my passion. I learned them, studied them, and continue sharing insights with you all on this blog, NoGenTech.
Among all the innovations I’ve explored, one stands out as the most transformative: Artificial Intelligence (AI). Imagine machines that can think, learn, and make decisions almost like humans: your phone predicting your next move, cars driving themselves, or computers diagnosing diseases.
AI is no longer a distant sci-fi dream; it’s shaping our world right now. In this beginner’s guide, I’ll break down AI in simple, digestible insights, revealing how it works, why it matters, and the future it’s building.
Key AI Usage & Impact Statistics
📈 The AI market surpassed $244 billion in 2025, up nearly $50 billion from 2023, and is projected to exceed $1 trillion by 2031. (Statista)
📈 More than 90% of AI in cybersecurity is expected to come from third-party providers, making advanced solutions easier to implement. (McKinsey & Company)
📈 Around six in ten Americans report wanting more authority over the ways AI is used in their everyday lives. (Pew Research)
📈 AI adoption has surged: 78% of organizations now use AI, up from 55% the previous year. (Stanford HAI 2025 AI Index)
📈 In education, 92% of students report using generative AI tools, with 18% admitting to submitting AI-generated work. (Forbes)
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the ability of a machine to think, learn, and make decisions like a human, or sometimes better than a human.
AI systems analyze data, identify patterns, and use those patterns to perform tasks such as recognizing faces, translating languages, predicting user behavior, or generating content.

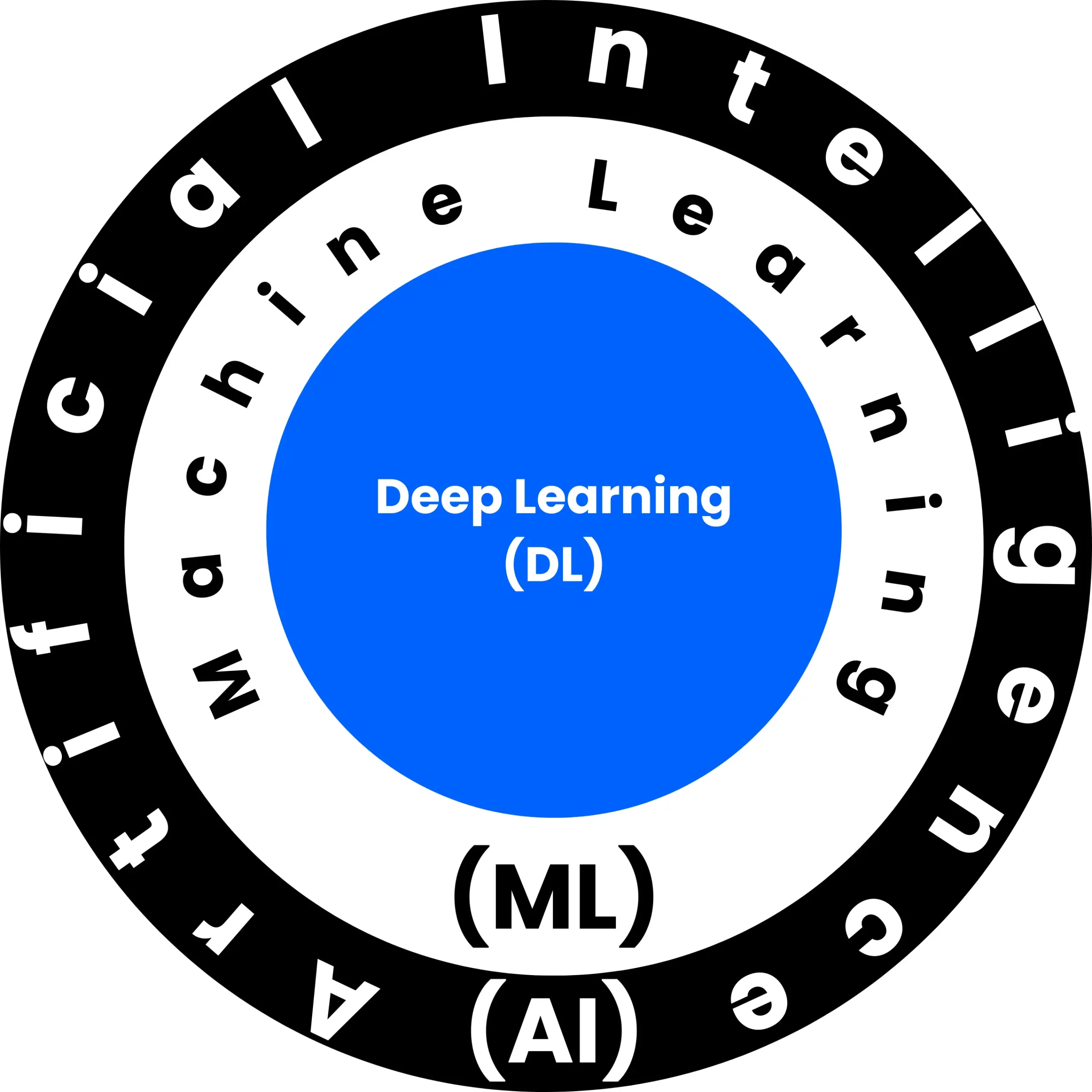
AI vs Machine Learning vs Deep Learning
- AI: The umbrella term for machines that perform intelligent tasks.
- Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI where machines learn from data without being explicitly programmed.
- Deep Learning (DL): A subset of machine learning using multi-layered neural networks that mimic the human brain, and enables advanced capabilities like image recognition and natural language understanding.
A Brief History of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Early Beginning of Artificial Intelligence (AI):
- 1950s – Alan Turing: Proposed the idea of machine intelligence and the famous “Turing Test.” (At Dartmouth Conference 1956)
- 1960s – Logical Systems: Early AI programs solved puzzles, played games, and performed symbolic reasoning.
AI Winters:
During the 1970s and late 1980s, funding and interest declined because AI systems failed to meet exaggerated expectations.
Rise of Machine Learning (2000s):
As data and computing power increased, machine learning became the backbone of modern AI.
Modern Era: Deep Learning and Generative AI
- 2010s: Deep learning advanced speech recognition, image processing, and language understanding.
- 2020s: Transformers and large language models (LLMs) led to generative AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, and Claude.
- 2025: AI is now integrated into everyday tools, business automation, and creative workflows.

Types of Artificial Intelligence
Based on Capability
- Narrow AI (Weak AI): Specialized for one task, e.g., chatbots, recommendation engines, or facial recognition.
- General AI (Strong AI): Hypothetical AI that could perform any intellectual task a human can do. Still under research.
- Super AI: A theoretical form of AI surpassing human intelligence, capable of independent reasoning and creativity.
The Classic Four Types Model
- Reactive Machines: Only react to input. No memory.
- Limited Memory: Learns from past data. Most modern AI falls here.
- Theory of Mind: Theoretical AI that understands emotions and intentions.
- Self-Aware AI: AI that has consciousness, still hypothetical.
Key Subfields of Artificial Intelligence
1. Machine Learning (ML)
The backbone of artificial intelligence, machine learning (ML) allows systems to learn from data without the need for explicit programming. ML techniques can be further divided into two categories: Unsupervised Learning and Supervised Learning.
2. Deep Learning
Inspired by the architecture of the human brain, deep learning is a branch of machine learning. Artificial Neural Networks are structures that roughly resemble the neural connections in human brains and are usable in deep learning to interpret complicated data, including audio, pictures, and spoken language.
3. Computer Vision
Gives robots the ability to “see” and understand the visual environment, usually used by autonomous vehicle companies. It enables features like facial recognition software to identify people and self-driving automobiles to identify objects on the road.
4. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP enables machines to communicate and understand human language. NLP is essential for machine translation tools, chatbots, and AI voice assistants like Alexa and Siri.

How Does Artificial Intelligence Work?

The process involves data acquisition, preprocessing, model training, and deployment — each step acting as an AI gateway that transforms raw data into actionable insights.
1. Data Acquisition
Collecting the information from which the AI system will learn is the initial stage. This information may originate from several sources, including sensors, user interactions, or big databases gathered specially for AI training.
2. Data Preprocessing
Before being used by the AI system, raw data must be cleaned up and formatted. This includes correction of errors, eradication of inconsistencies, and confirmation of a suitable data format to fit the selected techniques.
3. Model Selection
The kind of AI algorithm used will vary depending on the task. A recurrent neural network might be more appropriate for text sentiment analysis than a convolutional neural network for image identification.
4. Model Training
Here’s where things get magical. The preprocessed data is presented to the selected algorithm. The algorithm discovers patterns and links in the data by making several computations and modifications. This procedure can require a large investment of time and cloud computing power, particularly for complicated models.
5. Model Evaluation
After training, the AI model must be assessed to determine how well it is performing. This entails putting the model to the test on hypothetical data and gauging how well it performs the intended function. If the results are unacceptable, it could be necessary to retrain the model with additional data or make improvements to the model.
6. Deployment and Monitoring
The model incorporates practical applications if it is effective. This can entail integrating it into cloud computing platforms, hardware, or software. Consistently monitoring the model deployment’s performance is essential for ensuring it continues to function as expected.
Traditional Software vs Artificial Intelligence
| Feature | Traditional Software | Artificial Intelligence |
|---|---|---|
| Logic | Rule-based, fixed instructions | Learns from data and adapts |
| Adaptability | Cannot improve without reprogramming | Improves over time with training |
| Decision-making | Deterministic (if-then rules) | Probabilistic, based on patterns |
| Data Use | Limited | Can process massive datasets |
| Examples | Calculator, spreadsheets | Chatbots, self-driving cars, recommendation engines |
Challenges and Concerns in Artificial Intelligence
- Ethical Issues & Bias: AI can inherit biases from training data, leading to unfair outcomes in hiring, lending, or law enforcement.
- Job Displacement: Automation can replace certain human roles and requires reskilling and workforce adaptation.
- Transparency (Black Box Problem): Complex AI models often make decisions that are difficult to explain, reducing accountability.
- Data Privacy & Security: With massive data usage, AI ensures privacy and protection, which is a critical challenge.
How AI is Transforming the Future?
AI is not just reshaping industries; it’s setting the stage for a new era. Potential future applications include:
- Personalized Education: AI can adapt lessons to each student’s unique requirements and learning preferences.
- Environmental Sustainability: AI can help design sustainable tech, improve energy use, and forecast weather patterns to prevent natural disasters.
- Scientific Discovery: Artificial intelligence (AI) can assess enormous volumes of scientific data, speeding up research in disciplines like materials science and medicine.
- Human Augmentation: AI-driven assistive devices and prosthetics can improve the lives of those with impairments and increase human capacities.

Final Thoughts on Artificial Intelligence
AI is the way of the future. There will be a growing reliance on human oversight and development of AI systems, with the added responsibility of ensuring their ethical and prudent application.
The key lies in developing AI responsibly and ensuring that it remains transparent, fair, and aligned with human values.
Hopefully, this look into the field of AI will illuminate its inner workings and immense possibilities. It is an exciting moment to be alive as artificial intelligence (AI) develops, with many opportunities for a future in which intelligent machines coexist with humans.
People Also Ask
Is Artificial Intelligence safe?
AI is safe if used responsibly, but risks like bias and misinformation must be managed.
How do we use AI in daily life?
Through smart assistants, navigation apps, streaming recommendations, and fraud detection.
Can AI think like humans?
No, AI analyzes data but lacks emotions, consciousness, and reasoning like humans.
What skills are needed to work with AI?
Programming (Python/R), machine learning, data analysis, cloud computing, and AI ethics.
Can small businesses use AI?
Yes, AI tools like chatbots, marketing automation, and analytics platforms make it accessible and affordable for small businesses.




