Gripping Bitcoin Halving’s Stock-to-Flow Impact
In this cryptocurrency era, investors, traders, and relevant entities closely watch, analyze, and speculate upon Bitcoin’s performance. One of the key aspects that contribute to Bitcoin’s uniqueness and price dynamics is its halving event and the Stock-to-Flow ratio.
This blog post will shed light on the relationship between Bitcoin halving and the S2F ratio, exploring how these factors impact the world’s leading cryptocurrency. Navigating Bitcoin halving’s impact? Quantum Trade Wave provides strategic investment leverage. You can visit the website https://quantumtradewave.org/ to get started.
What is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin halving, or halvening, is an event that occurs almost every four years. During this event, the number of new Bitcoins mined per block is reduced by half. This process continues until the maximum supply of 21 million Bitcoins is reached. The latest Bitcoin halving occurred in May 2020, and the next is expected in 2024.
Stock-to-Flow: A Crucial Metric for Bitcoin
One of the most significant metrics used to analyze and understand the nature of Bitcoin is the Stock-to-Flow ratio. The concept of Stock-to-Flow originally gained popularity in the commodities market, where it was used to evaluate the scarcity of precious metals like gold and silver.
The Stock-to-Flow ratio signifies the amount of a given asset that is held in reserves (stock) relative to the yearly production rate (flow). For Bitcoin, the stock refers to the existing supply of coins in circulation, while the flow represents the new supply produced through the mining process in a specific time frame, usually one year.
Bitcoin’s Stock-to-Flow model gained prominence with the work of the pseudonymous analyst “PlanB.” He introduced the S2F ratio as a way to quantify the scarcity of Bitcoin and its potential impact on the price over time. According to the model, the higher the Stock-to-Flow ratio, the scarcer the asset, making it more valuable in theory.
The Stock-to-Flow ratio for Bitcoin has shown a unique pattern compared to traditional commodities. While precious metals like gold have relatively high Stock-to-Flow ratios due to their long-standing and stable supply, Bitcoin’s S2F ratio increases over time due to its fixed and predictable issuance schedule.
Read Also: Cryptocurrency Trading Bots: What are the Benefits and Limitations
As Bitcoin’s total supply is capped at 21 million coins, its Stock-to-Flow ratio increases with each halving event. Approximately every four years, the Bitcoin network undergoes a halving, a pre-coded event that halts miners’ block rewards in half. This halving process reduces the rate at which new coins are introduced into circulation, effectively decreasing the flow and amplifying the scarcity of the existing stock.
The Stock-to-Flow model suggests that Bitcoin’s shortage will continue to rise with each halving, eventually surpassing even precious metals like gold. Advocates of the model argue that this increasing scarcity will drive up the value of Bitcoin over time, leading to higher prices and potentially making it a viable hedge against inflation and economic uncertainties.
The Relationship Between Bitcoin Halving and Stock-to-Flow
One of the most intriguing aspects of Bitcoin’s monetary policy is the phenomenon of “halving.” Bitcoin halving is a pre-programmed event that occurs approximately every four years, effectively reducing the block rewards given to miners by half. This process is fundamental to Bitcoin’s design and plays a crucial role in managing its issuance rate and scarcity.
The relationship between Bitcoin halving and the Stock-to-Flow (S2F) ratio is tightly intertwined. The S2F ratio measures the scarcity of an asset by comparing the existing stock (total supply) with the flow (new supply) produced in a given period. As mentioned earlier, the Stock-to-Flow model is widely used in the commodities market to assess assets like gold and silver.
With each halving event, the flow of new Bitcoins entering the market is significantly reduced. This reduction in the flow has a profound impact on the Stock-to-Flow ratio of Bitcoin. As the flow decreases while the stock remains constant (or increases at a slower rate), the scarcity of Bitcoin naturally increases. This increase in scarcity is a pivotal aspect that draws the attention of investors and analysts alike.
One of the essential consequences of Bitcoin’s halving is the reduction in its inflation rate. The halving event ensures that the creation of new Bitcoins is a slow and predictable process, making it the first digital asset with a verifiable scarcity. In contrast, traditional fiat currencies are subject to central banks’ decisions, which can lead to unpredictable increases in money supply and inflation.
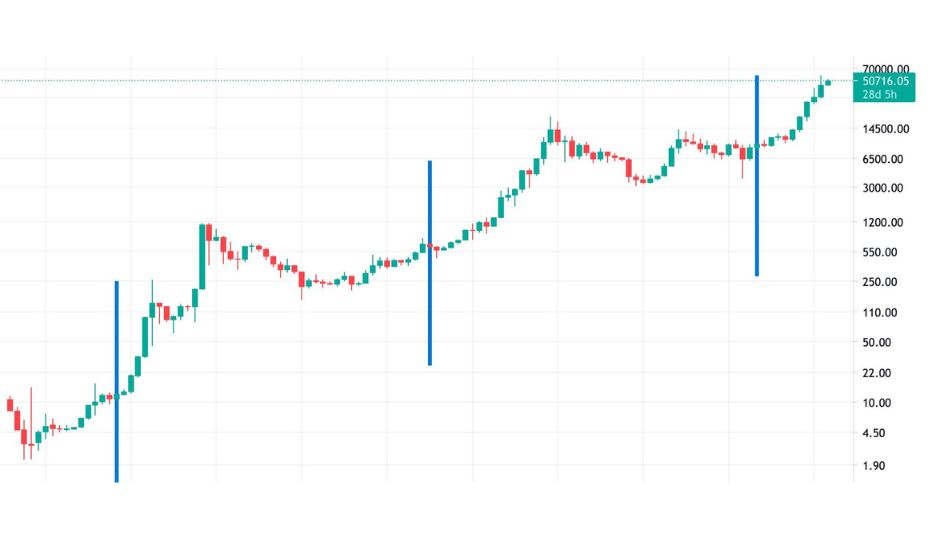
The unique relationship between halving and Stock-to-Flow has been observed in historical data. Previous halving events have led to significant price increases in the months and years following the reduction in block rewards. The idea behind this correlation is that as the flow decreases and scarcity increases, demand from investors and users remains constant or grows, leading to higher prices.
It’s important to note that the relationship between halving and Stock-to-Flow is not deterministic, and the cryptocurrency market is highly complex and influenced by various factors. While the Stock-to-Flow model suggests a positive correlation between scarcity and price, other elements such as market sentiment, macroeconomic trends, regulatory developments, and technological advancements also play vital roles in shaping Bitcoin’s price movements.
Bitcoin’s Price Trajectory
Bitcoin’s price trajectory has been influenced by halving events. Historically, these events have been followed by bull markets where the cryptocurrency’s value increased substantially. While past performance doesn’t guarantee future results, it highlights the correlation between scarcity and demand.
Conclusion
Bitcoin halving and the Stock-to-Flow ratio play a pivotal role in shaping the digital asset’s market dynamics. By reducing the issuance rate and increasing scarcity, halving events have historically impacted Bitcoin’s price. While the Stock-to-Flow model offers valuable insights, it is essential to consider other market factors in comprehending Bitcoin’s evolving and complex landscape.




