An Introduction to IoT – Uses, Benefits, and Challenges
The Internet of Things (IoT) is remodeling how we live, work, and interact with technology. Simply, from smart fridges that remind us to buy milk to massive industrial systems tracking inventory in real-time, IoT is everywhere. The IoT is a rapidly growing field that has the potential to revolutionize the way we live and work.
But what exactly is IoT? and how does it impact our world? In this article, I am going to discuss its uses, benefits, and the challenges it faces.
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a system of interconnected devices, objects, and people that are embedded with sensors, software, and network connectivity. These devices can collect and exchange data over the internet, without requiring human intervention.
IoT technology can enable devices to communicate with each other and with other internet-connected devices, such as cloud servers, to perform various tasks.
Top 10 Types of IoT:
IoT applications and technologies connect devices to the internet to gather, exchange, and analyze data. Different IoT types serve different sectors or use cases. The primary IoT types are:
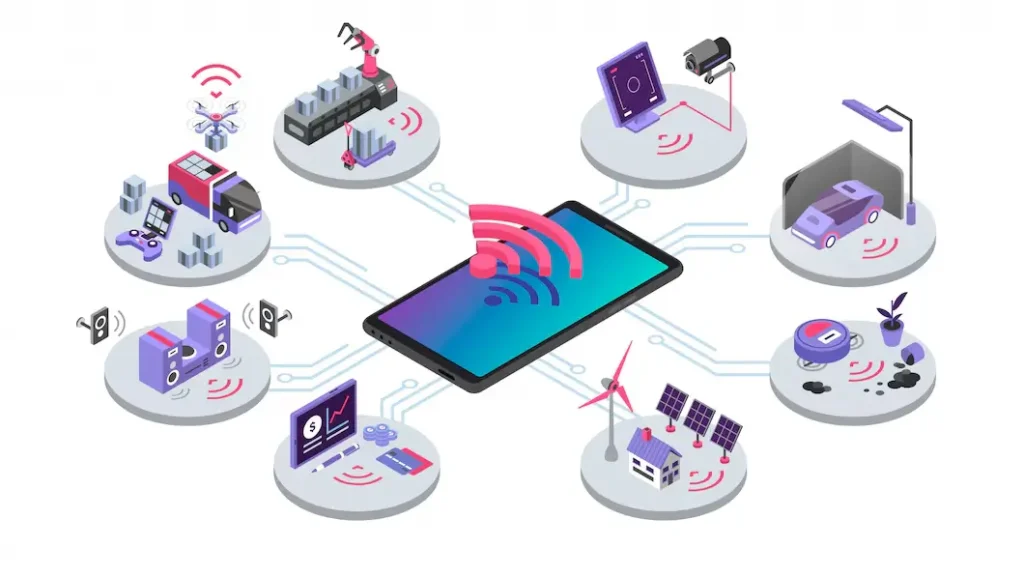
1. Consumer IoT (CIoT)
It refers to IoT applications used by individuals to enhance daily life, convenience, and home automation.
Examples:
- Smart home devices (thermostats, lights, security cameras, voice assistants)
- Wearables (smartwatches, fitness trackers)
- Smart appliances (fridges, washing machines, ovens)
2. Industrial IoT (IIoT)
Industrial IoT refers to the applications in industrial sectors to improve manufacturing processes, operations, and efficiency.
Examples:
- Smart factories and automation systems
- Predictive maintenance in machinery
- Supply chain management and inventory tracking
- Energy management systems
3. Commercial IoT
IoT systems are used in businesses for operational efficiency, customer service, and building management.
Examples:
- Smart building systems (heating, lighting, security)
- Retail analytics (smart shelves, inventory tracking)
- Environmental monitoring for businesses
4. Healthcare IoT (Health IoT or IoMT)
IoT in healthcare is aimed at improving patient care, medical diagnostics, and hospital operations.
Examples:
- Wearables that monitor health metrics (heart rate, glucose levels)
- Remote patient monitoring devices
- Smart medical devices (smart inhalers, blood pressure monitors)
- Hospital asset tracking systems
5. Agriculture IoT (AgriTech)
This kind of IoT in agriculture for smarter farming, resource management, and crop monitoring.
Examples:
- Smart irrigation systems
- Crop monitoring and soil sensors
- Livestock tracking
- Climate and weather condition monitoring
6. Smart City IoT
Such IoT is used in urban infrastructure to improve public services, optimize energy use, and ensure better city management.
Examples:
- Traffic management systems (smart traffic lights, congestion monitoring)
- Waste management (smart bins, recycling monitoring)
- Public safety systems (smart surveillance cameras)
- Smart grids for energy distribution
7. Automotive IoT (Connected Vehicles)
IoT applications in the automotive industry that improve vehicle performance, safety, and user experience.
Examples:
- Autonomous vehicles (self-driving cars)
- Telematics and fleet management systems
- Vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication systems
- Remote diagnostics and predictive maintenance for vehicles
8. Energy IoT
Efficiency and sustainability in energy generation, distribution, and consumption were achieved through the usage of the Energy Internet of Things (EIoT).
Examples:
- Smart meters for electricity, gas, and water consumption
- Renewable energy management (solar, wind)
- Smart grid technologies
- Energy-efficient building systems
9. Logistics and Supply Chain IoT
These logistics and supply chain management IoT technologies track items, enhance delivery, and boost efficiency.
Examples:
- GPS-enabled fleet tracking
- RFID-based inventory tracking
- Smart warehouses with automated systems
- Cold chain monitoring for temperature-sensitive goods
10. Military and Defense IoT (IoMT)
Defense and military organizations utilize IoT to improve operational efficiency, situational awareness, and safety.
Examples:
- Drones and unmanned vehicles
- Remote surveillance systems
- Tactical wearables for soldiers (e.g., body sensors)
- Smart weapons and equipment
Top Uses of IoT:
IoT technology is being used in various industries, including healthcare, agriculture, manufacturing, transportation, and smart home, to enhance productivity and efficiency. Here are some of the most common uses of IoT:

1. Healthcare:
IoT devices such as wearable fitness trackers, glucose monitors, and blood pressure monitors can help people monitor their health and share their health data with their doctors. Healthcare professionals can use this data to track and manage their patients’ health.
2. Agriculture:
IoT devices such as soil moisture sensors, weather monitors, and GPS trackers can help farmers optimize their crop yields and reduce waste. The data collected by these devices can help farmers make informed decisions about when to plant, irrigate, and harvest their crops.
3. Manufacturing:
IoT devices can help manufacturers optimize their production processes by monitoring equipment performance, tracking inventory, and managing the supply chain. IoT technology can also enable predictive maintenance, which can reduce downtime and increase productivity.
4. Transportation:
The IoT technology in the transportation industry can optimize routes, track shipments, and monitor vehicle performance. This can help reduce transportation costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction.
5. Smart homes:
IoT devices such as smart thermostats, smart lighting, and smart security systems can make homes more energy-efficient and secure. These devices can be controlled remotely using a smartphone or a voice assistant. This makes it easy for homeowners to manage their homes from anywhere.
Benefits of IoT:
IoT technology offers numerous benefits, including:
1. Improved efficiency:
IoT technology can help automate various tasks, reducing the time and resources required to perform them. This can help businesses become more efficient and increase productivity.
2. Increased safety:
IoT devices have the potential to save lives, as they can detect and alert users of any impending risks like fires, floods, or gas leaks. Through their vigilance, serious accidents are avoided and countless people remain safe from harm.
3. Cost savings:
Utilizing IoT technology can assist businesses in saving money and boosting their profits by optimizing processes, curtailing wastefulness, and elevating efficiency. These advantages not only reduce costs but also open new horizons of growth for organizations.
4. Enhanced customer experience:
IoT devices can help businesses provide a better customer experience by offering personalized services, such as customized recommendations, based on customer data.
5. Real-time monitoring:
IoT devices can provide real-time monitoring of various processes, such as equipment performance and inventory levels. This can assist businesses in quickly pinpointing and addressing issues, thereby boosting operational efficiency.
6. Improved decision-making:
We can also utilize IoT technology to give businesses, an ability to enable real-time data and hence enable them to make the right decisions. This solution will help increase the efficiency of your business and achieve better financial results.
7. Sustainability and Environmental Benefits:
For this reason, IoT can actively participate in environmental conservation by minimizing energy wastage, disposal of products, and monitoring weather conditions. Smart grids also combine effectiveness in distribution while IoT is applied in devices that can monitor and minimize water usage or even detect pollutant presence.
8. Predictive Maintenance:
Smart systems can precisely estimate when a particular piece of equipment is due for a failure based on the information generated in real-time and that of similar systems that have been in the past. This enables organizations to apply fixed methods before a problem arises, meaning minimized working breaks and repair expenses.
9. Remote Accessibility:
IoT devices allow users to monitor and control devices remotely. This is especially beneficial in healthcare, where wearable devices can send patient data to doctors in real time, or industrial settings, where machinery can be managed from afar.
10. Better Supply Chain Management:
As will be seen IoT technology improves supply chain transparency since it follows goods as they are transported. Real time tracking allows businesses to prevent delays and know the right way to handle the products.
Challenges of IoT:
While IoT technology offers numerous benefits, it also poses several challenges, including:
1. Security:
IoT devices are sadly prone to hacking and cyberattacks, jeopardizing the security of any confidential information they contain as well as compromising people’s safety.
2. Interoperability:
IoT devices often use different protocols and standards, which can make it challenging to connect them and exchange data. It also introduces complexities when it comes to developing applications that can interact with multiple devices.
3. Data privacy:
IoT devices collect vast amounts of data, which can be used by third parties without users’ consent. This raises concerns about how the data is stored, shared, and used.
4. Data storage:
IoT devices generate huge amounts of data that need to be properly stored in order to make use of it. This can be challenging for businesses, as it requires adequate storage capabilities and reliable data management systems.
5. Data management:
IoT devices generate vast amounts of data, which can be challenging to manage and analyze. Businesses need to have the infrastructure and expertise to handle and make sense of this data.
6. Compatibility:
Some IoT devices may not be compatible with existing systems and infrastructure, requiring businesses to make significant investments in upgrading their systems. This can raise costs and limit the scalability of the system.
7. Scalability:
As the number of Internet of Things devices increases, businesses need to be able to scale their infrastructure and systems to handle the increased load.
8. Reliability:
IoT devices can fail or malfunction, leading to downtime and disruptions. Businesses need to have contingency plans in place to minimize the impact of such failures.
Final Verdict
Internet of Things (IoT) is a rapidly growing field that offers numerous benefits, including improved efficiency, increased safety, cost savings, enhanced customer experience, and real-time monitoring.
However, IoT also poses several challenges, including security, interoperability, complexity, privacy, data management, compatibility, scalability, and reliability. To fully realize the benefits of IoT, businesses need to carefully evaluate their needs, invest in the right infrastructure and expertise, and address the challenges posed by this technology.